Managing customer data sounds simple until it isn’t. Many small and medium businesses start with spreadsheets because they are familiar, flexible, and easy to setup. But as customer interactions grow, follow-ups multiply, and teams expand; spreadsheets often start to feel limiting.
That’s where CRM systems come in. Spreadsheet vs CRM debate isn’t about which tool is better. It's about which one fits your current business needs and future growth. This blog breaks down how spreadsheets and CRMs differ, where each one works best, and how to decide when it’s time to move from one to the other.
What Is a Spreadsheet?
A spreadsheet is a digital table used to store and organize data in rows and columns. Tools like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are widely used for tracking customer information, sales data, expenses, and more. Spreadsheets are popular because they are easy to use, highly customizable, require low or no cost, and are familiar to almost everyone. For small teams or those who operate alone, spreadsheets often feel like the quickest way to get started.
However, spreadsheets fell short because they are not specifically designed to manage customer relationships. They need to be updated manually, lack automation, and it becomes difficult to maintain them as data volume increases.
Core Functions of Spreadsheets
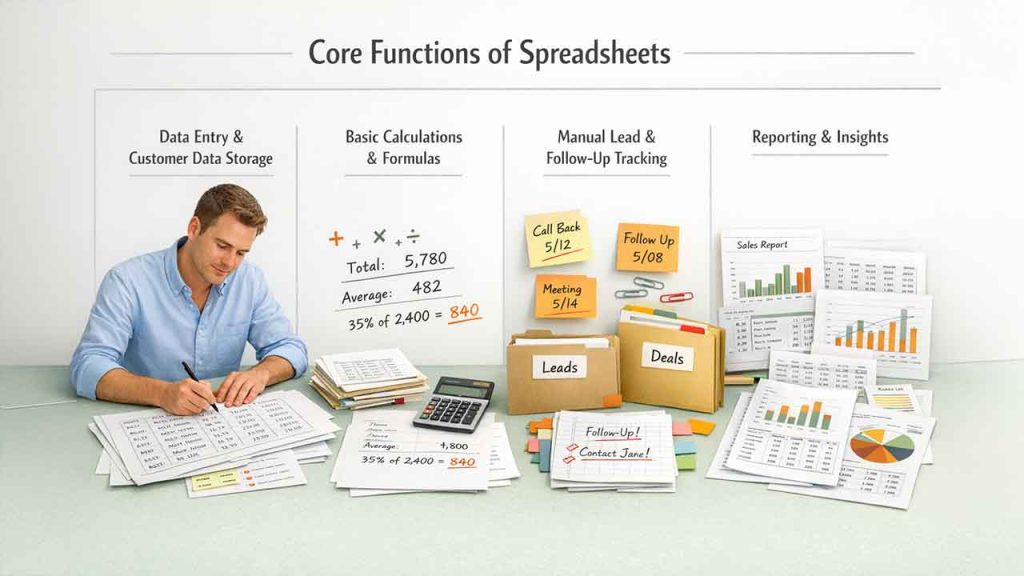
Data Entry and Customer Data Storage
In spreadsheets, you can manually enter details such as customer names, email addresses, and contact numbers, along with other details. This works well for managing small datasets; however, it becomes time-consuming, andthe chances of error increase as records grow.
Basic Calculations and Formulas
Spreadsheets can perform basic calculations such as totals, averages, and growth percentages using predefined formulas. This is helpful to businesses as they can analyze simple sales or revenue data.
Manual Lead and Follow-Up Tracking
Users can also add notes or color-code cells. This helps them track leads, deals, or follow-ups. However, this process requires heavy manual effort and discipline.
Reporting and Insights
Spreadsheets can generate charts and tables, but advanced reporting requires complex formulas. It also lacks real-time updates.
Limitations of Using Spreadsheets

Small to medium size businesses often use spreadsheets as a starting point to manage customer data, but they pose certain limitations as business operations grow. Spreadsheets are useful for basic tracking; however, they are not built for managing relationships, workflows, or real-time collaboration.
Lack of Automation and Workflow Management
Spreadsheets are entirely dependent on manual updates. Tasks like follow-ups, reminders, lead assignments, and activity tracking must be handled separately and effectively. This manual effort often results in missed opportunities, inconsistent processes, and revenue lost in businesses.
High Risk of Data Errors and Duplicate Records
There is a high risk of data errors in spreadsheets. Because they are manually edited, it can cause errors such as accidental deletions, incorrect entries, and duplicate records. With the growing data, maintaining accuracy becomes essential in which spreadsheets fail. Tracking sales and communicating with customers also becomes difficult due to these mistakes or errors.
Limited Team Collaboration
Version conflicts and overwriting issues are common when multiple users work on the same spreadsheet at once. Unlike CRM systems, spreadsheets lack role-based access, activity logs, and real-time collaboration features.
Poor Scalability for Growing Businesses
For a small contact list, spreadsheets may work just fine. However, they quickly become difficult to manage when there’s an increase in customer data. Searching, filtering, and updating large datasets hinders productivity and makes reporting difficult.
No Built-In Customer History or Insights
Spreadsheets only store data in their raw form. They do not provide any insights. It lacks an easy way to track communication history, analyze customer behavior, or deal with stages. This makes it difficult to build long-term relationships with customers.
Understanding CRM
What is CRM? A CRM (customer relationship management) system is software designed specifically to manage customer data, interactions, sales pipelines, and communication history in one centralized platform.
Unlike spreadsheets, CRMs don’t just store data; they actively help you by:
- Tracking leads and deals
- Automating follow-ups
- Monitoring customer activity
- Improving sales and supporting workflows
CRMs are built for growing businesses that need structure, visibility, and collaboration.
Core Functions of CRM
CRM systems do more than just store customer data. They are specially designed for businesses to assist them with building strong relationships, improve efficiency, and grow without any chaos.
Centralized and Accurate Customer Data
The biggest advantage that CRM provides is organizing and storing all customer information in one place. There is no need to manage multiple spreadsheets, emails, and notes. With CRM, teams can access a single customer profile which contains all updated information about that client. This eliminates all duplicate records which reduces confusion and allows teams to work more efficiently. This reduces confusion and ensures everyone works with accurate data.
Improved Sales Productivity and Pipeline Tracking
CRMs organize leads, tracks deal stages and set reminders for follow-ups. This helps streamline the sales process. This way sales teams don’t have to rely on memory, guesswork, or manual tracking. This structure is helpful to them as they can focus entirely on high-value prospects and close deals faster.
Automation That Saves Time and Reduces Errors
CRM automates routine tasks such as scheduling follow-up reminders, email logging, and assigning leads. It reduces manual work and human error while freeing teams to focus on other meaningful tasks, such as strategy planning and relationship building. Modern AI CRM tools enhance this automation even further with predictive analytics and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
Better Customer Experience and Personalization
CRMs provide full visibility into past interactions, preferences, and issues. Using this visibility, businesses can personalize communication. This makes customers feel understood and valued.
CRM Scalability for Business Growth
Unlike spreadsheets, CRMs are built to grow with your business. It doesn’t matter whether you manage 50 customers or 50,000; the system stays organized and efficient.
CRM Reporting and Analytics
CRM platforms provide dashboards and generate detailed reports that offer actionable insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and team productivity.
Team Collaboration
It provides a shared workspace for sales, marketing, and support teams. They can access the same accurate and up-to-date data to enhance customer experience while improving internal coordination.
Spreadsheet vs CRM: Key Differences
| Feature | Spreadsheet | CRM System |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Basic data storage & manual tracking | Centralized customer relationship management |
| Ease of Use | Simple for small datasets | User-friendly with guided workflows |
| Automation | No automation | Automated follow-ups, reminders & workflows |
| Data Accuracy | High risk of errors & duplicates | Built-in validation & duplicate detection |
| Customer History | Not available | Complete interaction & activity tracking |
| Reporting & Analytics | Manual formulas & charts | Advanced reports & dashboards |
| Scalability | Poor scalability as data grows | Designed to scale with business growth |
| Integration Capabilities | Minimal or manual | Seamless integration with email, marketing & sales tool |
| Best For | Individuals or very small teams | Growing businesses & sales-driven teams |
When Using a Spreadsheet Makes Sense
For early-stage needs, spreadsheets offer simplicity and low cost. Spreadsheets can still be useful in certain situations:
- Very small businesses or solo founders
- Simple contact lists
- Short-term projects
- Minimal customer interaction
When Your Business Needs a CRM System
A CRM becomes essential when:
- You manage many leads or customers
- Multiple team members access customer data
- Follow-ups and sales tracking are critical
- Customer experience and retention matter
- You plan long-term growth
If you're ready to move beyond manual processes, automating everyday business operations is the logical next step for sustainable growth.
Spreadsheet vs CRM: Real-World Use Cases
Understanding how spreadsheets and CRMs perform in real situations makes the difference clearer.
Small Freelancers and Solo Entrepreneurs
Many freelancers often use spreadsheets in the early stages to keep track of their clients, payments, and deadlines. However, when the number of projects increases to a point where spreadsheets get cluttered, it becomes difficult to manage workflow. In this situation, using a CRM helps them track conversations and follow-ups with their clients as well as repeat clients without missing opportunities.\
Startups and Growing Sales Teams
Startups commonly rely on spreadsheets during early stages. But, as the sales team grows, spreadsheets will no longer be sufficient to track sales pipelines or support collaboration. However, a CRM enables the sales team to share updates in real-time, track deal progress, and accurately provide revenue forecasts.
Customer Support and Service Teams
Using a spreadsheet to manage customer support quickly becomes messy or chaotic. CRMs help customer support teams log every ticket, interaction, and resolution for customer queries, allowing for a faster response time and a higher level of consistency.
Marketing and Lead Management
Spreadsheets struggle to track lead sources and engagement. CRMs connect leads to campaigns, showing what actually converts and helping marketers make data-driven decisions.
SEO and Link Building Teams
For specialized areas like SEO and guest posting, standard CRMs often fall short. These teams need advanced automation to track link placements, manage publisher relationships, and monitor outreach campaigns at scale. Some platforms have evolved into “learned CRM” systems that improve through customer interactions and payment behaviors. GuestPostCRM, for instance, uses AI to filter spam, predict publisher quality, and maintain content standards, showing how CRMs can move beyond data storage into intelligent decision-making tools.
How to Choose Between a Spreadsheet and a CRM System
Ask yourself:
- Is customer data central to my business?
- Do I need automation and reminders?
- Will my data grow over time?
- Do multiple people need access?
If the answer is yes to most, a CRM is the better choice.
Final Verdict: Spreadsheet vs CRM
There’s an ongoing debate on whether to use spreadsheets or a CRM system when running a business. The debate of spreadsheet vs CRM isn’t about which tool is better; it’s about which fits your business goals and stages. While spreadsheets help track short-term work with limited data; it won’t provide support in the long run as your business grows.
A customer relationship management system (CRM) is designed for long-term success. They offer automation, accuracy, collaboration, and visibility into insights that spreadsheets will never be able to compete with. For any business that takes its customer relationships seriously and wants to boost sales growth; having a CRM is not simply an upgrade, it’s a necessity.
FAQs for Spreadsheet vs CRM
Q. Can a spreadsheet replace a CRM?
A. Spreadsheets can handle basic data storage, but they lack automation, scalability, and customer insights offered by CRMs.
Q. Is CRM expensive compared to spreadsheets?
A. While spreadsheets are cheaper upfront, CRMs save time, reduce errors, and improve sales efficiency in the long run.
Q. Do small businesses need a CRM?
A. Yes, especially if they manage multiple customers, follow-ups, or sales pipelines.
Q. What is the biggest drawback of spreadsheets?
A. Manual data entry and a high risk of errors as data grows.
Q. Can I migrate from the spreadsheet to CRM later?
A. Yes, most CRM platforms allow easy import of spreadsheet data.





.png)
.png)


.png)